VIO Server Howto
Contents
IOS - Information and Maintenance
Virtual Devices: Storage
- List unmapped disks
- List all Disk Mappings
- Create a Virtual SCSI Host Adapter
- Remove a Virtual SCSI Host Adapter
- Assign a Disk/LV to a Virtual SCSI Host Adapter
- Unassign a Disk/LV from a Virtual SCSI Host Adapter
Virtual Devices: Fibre Channel
- Create a Virtual Fibre Channel Adapter
- List Virtual Fibre Channels
- List NPIV Capable Ports
- Assign a Physical FC Adapter to a Virtual Fibre Channel Adapter
- Unassign a Physical FC Adapter from a Virtual Fibre Channel Adapter
Virtual Devices: Network
- List Shared Ethernet Adapters
- Create a Shared Ethernet Adapter
- Enable SEA Load Sharing Mode
- Perform a Manual SEA Failover
- Show SEA Satus
- List Links on Physical Ethernet Adapters
- Set a local IP Address
- Remove a local IP Address
1. Run IOS commands as root
According to IBM you should never work as root on VIO servers. However, if you login as user padmin and type
oem_setup_env
you get the root credentials (without even been asked for a password).
By default the ioscli commands are not available for the root user. All ioscli commands are in fact calls of /usr/ios/cli/ioscli with the command as argument. You see this if you list the aliases of the padmin user.
Knowing this you can use all ioscli commands as user root by appending /usr/ios/cli/ioscli. Instead of »lsmap -all« you would type
root@vios# /usr/ios/cli/ioscli lsmap -all
If you set an alias
alias i=/usr/ios/cli/ioscli
you could even type
root@vios# i lsmap -all
2. What is the AIX command behind an ioscli command?
If you want to know what AIX command is behind the command you issued as user padmin you can use a special debug mode:
$ export CLI_DEBUG=33
That's the output of the lsnports command in this mode:
$ lsnports AIX: "/usr/lib/methods/viosmgr -t npiv -f query_fc_ports >/dev/null" name physloc fabric tports aports swwpns awwpns fcs0 U789C.001.DQDH231-P1-C2-T1 1 64 64 2048 2047 fcs1 U789C.001.DQDH231-P1-C2-T2 1 64 62 2048 2043
IOS - Information and Maintenance
1. List all ioscli commands
$ help
You can type
$ help <command>
to display a command's syntax, e.g
$ help lsmap
Usage: lsmap {-vadapter ServerVirtualAdapter | -plc PhysicalLocationCode |
-all} [-type BackingDeviceType ... | -net | -npiv ]
[-field FieldName ...] [-fmt delimiter]
lsmap -ams {-vtd PagingDevice | -all}
[-type BackingDeviceType ... ]
[-field FieldName ...] [-fmt delimiter]
lsmap -clustername ClusterName {-all | -hostname}
Displays the mapping between physical and virtual devices.
-all Displays mapping for all the server virtual adapter
devices. Defaults to VSCSI adapter devices.
-clustername Specifies the cluster name.
-hostname Specifies the host name.
-vadapter Specifies the server virtual adapter device
by device name.
-plc Specifies the server virtual adapter device
by physical location code.
-vtd Specifies the (AMS)Active Memory Sharing
Paging Device to be displayed.
-type Specifies to display virtual devices whose backing
device matches the type given.
-net Specifies supplied device is a virtual server
Ethernet adapter.
-npiv Displays NPIV binding information.
-ams Displays (AMS)Active Memory Sharing paging space
device information.
-field Specifies a list of fields to be displayed.
-fmt Divides output by a user-specified delimiter.
2. IOS Version
$ ioslevel 2.2.0.10-FP-24
3. Apply IOS Fixes
Put the IOS fixes somewhere in a local directory or on an NFS server (e.g. /mnt/iosfixes). Then run
$ updateios -dev /mnt/iosfixes -accept
4. IOS Upgrade Procedure
It is highly recommended first to clone the running installations to free disks (here: hdisk2 and hdisk3). That way we can always go back to the old working installation:
$ oem_setup_env # alt_disk_copy -B -d "hdisk2 hdisk3" # exit
Read the release notes. You may need to upgrade the VIO server in two steps (e.g. first to 2.2.2.1 and than further to 2.2.2.5).
Then put the IOS upgrade packages somewhere in a local directory or on an NFS server (e.g. /updates/2.2.2.5) and run
$ updateios -commit $ updateios -dev /updates/2.2.2.5 -accept -install $ shutdown -restart
5. Reboot the VIO Server
$ shutdown -restart
Virtual Devices: Storage
1. List unmapped disks
$ lspv -free NAME PVID SIZE(megabytes) hdisk24 none 8631 hdisk25 none 8631 hdisk26 none 8631 hdisk27 none 8631
 Warning:
If you use vendor specific device drivers (such as the SDD or EMC drivers) you see all
hdisks as free. You have to limit the list to your logical devices, e.g.
Warning:
If you use vendor specific device drivers (such as the SDD or EMC drivers) you see all
hdisks as free. You have to limit the list to your logical devices, e.g.
$ lspv -free | grep vpath
2. List all Disk Mappings
$ lsmap -all SVSA Physloc Client Partition ID --------------- -------------------------------------------- ------------------ vhost1 U9117.570.65E12FB-V1-C102 0x0000000a VTD vtscsi1 LUN 0x8100000000000000 Backing device hdisk6 Physloc U7879.001.DQDHXYN-P1-C4-T1-W50050763041302AA-L4021400000000000 VTD vtscsi8 LUN 0x8200000000000000 Backing device hdisk14 Physloc U7879.001.DQDHXYN-P1-C4-T1-W50050763041302AA-L4031400100000000
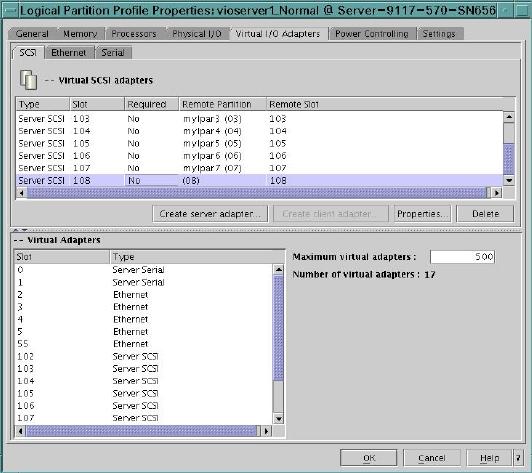
3. Create a Virtual SCSI Host Adapter
This has to done on the HMC for the profile of the VIO server: You create a new Virtual SCSI Host-Adapter and assign it only to your client LPAR.
The same slot ID should then be assigned to a new client adapter in the client LPAR's profile.
You can do these steps dynamically to avoid a restart of the VIO server. Use the Dynamic Logical Partitioning option for that. If you go for the dynamic option don't forget to do the same assignments in the profiles aswell, otherwise your LPAR loses all storage after a new start of the VIOS!
After dynamically adding the server hostadapters you have to rerun the configuration mamager before you can see the new vhost device:
$ cfgdev
4. Remove a Virtual SCSI Host Adapter
$ rmdev -dev vhostX [ -recursive ]
The option »-recursive« can be used to remove all still attached child devices.
Then remove the adapters dynamically from the VIO server aswell as from the VIOS' profile.
5. Assign a Disk/LV to a Virtual SCSI Host Adapter
To map hdisk22 to vhost1 just type
$ mkvdev -vdev hdisk22 -vadapter vhost1 vtscsi19 available
The VIO server assigns the next free number (19 here) and creates the mapping device vtscsi19. But you can specify your own name for the mapping device by making use of the »-dev« option:
$ mkvdev -vdev hdisk22 -dev vthdisk22_barney -vadapter vhost1 vthdisk22_barney available
If you use LVs rather than whole disks or LUNs the same rules apply:
# default mapping device$ mkvdev -vdev lpar21_lv03 -vadapter vhost1 vtscsi19 available# custom mapping device$ mkvdev -vdev lpar21_lv03 -dev vtdisk21_lv03 -vadapter vhost1 vtdisk21_lv03 available
6. Unassign a Disk/LV from a Virtual SCSI Host Adapter
$ rmvdev -vtd vtscsiXX
Virtual Devices: Fibre Channel
IBM introduced the support of NPIV technology with VIOS (Virtual I/O Sever) 2.1 with a client AIX running either AIX 5.3 TL9 or later, or AIX 6.1 TL2 or later, or AIX 7.1. Earlier releases are not supported.
1. Create a Virtual Fibre Channel Adapter
This has to done on the HMC for the profile of the VIO server: You create a new Virtual Server Fibre Channel adapter and assign it to only one client LPAR.
The same slot ID should then be assigned to a new Client Fibre Channel adapter in the client LPAR's
profile.
2. List Virtual Fibre Channels
$ lsmap -all -npiv Name Physloc ClntID ClntName ClntOS ------------- ---------------------------------- ------ -------------- ------- vfchost0 U8203.E4A.05A6DD1-V1-C41 3 mylpar6 AIX Status:LOGGED_IN FC name:fcs1 FC loc code:U789C.001.DQDH231-C3-T2 Ports logged in:2 Flags:a<LOGGED_IN,STRIP_MERGE> VFC client name:fcs0 VFC client DRC:U8203.E4A.05A6DD1-V3-C41-T1 Name Physloc ClntID ClntName ClntOS ------------- ---------------------------------- ------ -------------- ------- vfchost1 U8203.E4A.05A6DD1-V1-C43 4 mylpar8 AIX Status:LOGGED_IN FC name:fcs1 FC loc code:U789C.001.DQDH231-C3-T2 Ports logged in:2 Flags:a<LOGGED_IN,STRIP_MERGE> VFC client name:fcs0 VFC client DRC:U8203.E4A.05A6DD1-V4-C43-T1
3. List NPIV Capable Ports
NPIV = N_port ID Virtualization
$ lsnports name physloc fabric tports aports swwpns awwpns fcs0 U789C.001.DQDH231-P1-C2-T1 1 64 64 2048 2047 fcs1 U789C.001.DQDH231-P1-C2-T2 1 64 62 2048 2043
4. Assign a Physical FC Adapter to a Virtual Fibre Channel Adapter
$ vfcmap -vadapter vfchost0 -fcp fcs1
5. Unassign a Physical FC Adapter from a Virtual Fibre Channel Adapter
There isn't a separate command for this action - you just leave the argument after
-fcp empty:
$ vfcmap -vadapter vfchost0 -fcp
Virtual Devices: Network
1. List Shared Ethernet Adapters
$ lsmap -all -net SVEA Physloc ------ -------------------------------------------- ent12 U9117.570.65E12FB-V2-C20-T1 SEA ent13 Backing device ent3 Physloc U7311.D20.651372C-P1-C01-T2
2. Create a Shared Ethernet Adapter
To create a Shared Ethernet Adapter (SEA) you need:
- a physical adapter as backend: <PHYS>
- a virtual adapter as defined in the VIOS' profile: <VIRT>
- an internal VLAN ID: <VLAN>
- a second virtual adapter as defined in the VIOS' profile: <CONT>
# simple:$ mkvdev -sea <PHYS> -vadapter <VIRT> -default <VIRT> -defaultid <VLAN># Shared Ethernet Adapter Failover:$ mkvdev -sea <PHYS> -vadapter <VIRT> -default <VIRT> -defaultid <VLAN> -attr ha_mode=auto ctl_chan=<CONT>
Example: To create a Shared Ethernet Adapter on top of an virtual adapter ent11 using VLAN 20, the physical adapter ent2 as backend, and the virtual adapter ent13 for the control channel type:
$ mkvdev -sea ent2 -vadapter ent11 -default ent11 -defaultid 20 -attr ha_mode=auto ctl_chan=ent13
3. Enable SEA Load Sharing Mode
First on the primary SEA, then on the secondary:
$ chdev -dev <SEA> -attr ha_mode=sharing
4. Show SEA Satus
Let's say for the SEA ent20:
$ entstat -all ent20 | grep '^[ ]*State'
State: PRIMARY
Other possible states: BACKUP, PRIMARY_SH, BACKUP_SH. The states PRIMARY_SH and BACKUP_SH are indicating that Load Sharing Mode has been enabled.
5. Perform a Manual SEA Failover
To perform a failover for the SEA ent20 go to the active side ("State: PRIMARY") and type:
$ chdev -dev ent20 -attr ha_mode=standby
The SEA on the other VIO server automatically becomes active. To switch back you would type
$ chdev -dev ent20 -attr ha_mode=auto
6. List Links on Physical Ethernet Adapters
$ netstat -cdlistats | grep -Ei "\(ent|media|link status" ETHERNET STATISTICS (ent3) : Link Status : Up Media Speed Selected: 100 Mbps Full Duplex Media Speed Running: 100 Mbps Full Duplex
7. Set a local IP Address
To configure an local IP 192.168.1.2 address to en0 use
$ mktcpip -hostname <HOSTNAME> \
-inetaddr 192.168.1.2 \
-interface en0 -start \
-netmask 255.255.255.0 \
-gateway <GATEWAY>
8. Remove a local IP Address
If you want to remove the IP configuration from en0, type
$ rmtcpip -interface en0
 unixwerk
unixwerk